Transportation plays a major role in the modern era. According to International Energy Agency (IEA) report, fossil fuel-based vehicles are the second largest source of CO2 emissions. Nearly 72% of the total global oil demand is utilized by the transportation sector. Due to the depleting fossil fuel resources along with increased concern on environmental pollution, there is a trend towards the usage of electric vehicles.
An electric vehicle basically consists of a battery which supplies an electric motor to drive the wheels. The battery is charged either from the external supply like grid or it can be charged during regenerative braking. As battery cannot store more energy, EVs are limited to short range. In order to increase the range of the vehicle, Internal Combustion Engine is included in some EVs. Depending on the drive system, there are three types of electric vehicle:
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) and
- Plugin Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV):
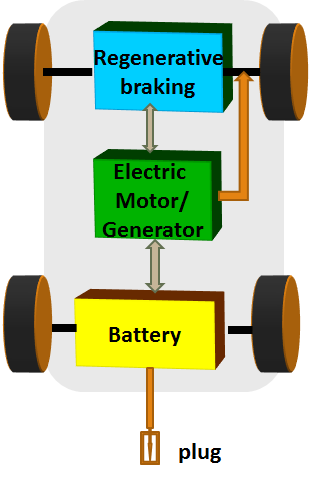
A battery electric vehicle runs entirely using an electric motor and battery. The battery supplies an electric motor to drive the wheels. The battery can be charged from the grid power supply and hence this vehicle can be easily charged in home. In addition, when applying brake, the regenerative power can be stored in batteries. As only an electric motor is used, there is no combustion related emissions from the vehicle and electric motor enables to achieve a fast and smooth acceleration. However, as batteries cannot store more charge, they have a shorter range than the ICE vehicles. But it is found that most of the customers drive within the range of a battery electric vehicle, and it is widely preferred for short distance travel. Though the initial cost is higher than the ICE vehicle, in long run EV will be cheaper as it does not require any fuel cost and maintenance.
Some of the BEV vehicles in market are Audi e-tron, BMW i3/i3s, Hyundai Kona electric, Tesla Model S, Tesla Model X, Tesla Model Y.
2. Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
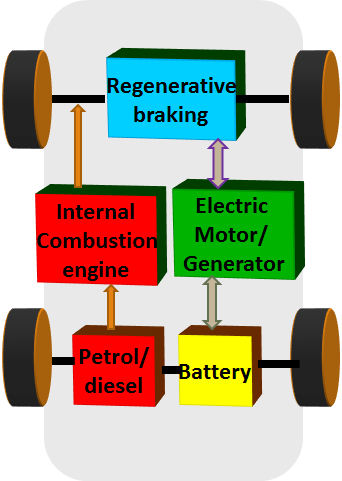
Hybrid Electric Vehicles as the name indicates it has both Internal Combustion engine and an electric motor. The Internal Combustion engine is fed from petrol/gasoline and battery supplies the electric motor. The electric motor assists the ICE to drive the wheels and therefore a smaller IC engine can be used. The control of HEV is complex as two complementary drive systems are involved. The battery is charged during regenerative braking or through the energy generated by the ICE. There is no provision to charge the battery from external supply.The two-drive system helps to achieve a longer range than BEV but emission problem persists due to the fuel requirement for ICE.
Some of the HEV vehicles in market are Toyota Prius, Ford Escape Hybrid, and Ford Fusion.
3. Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
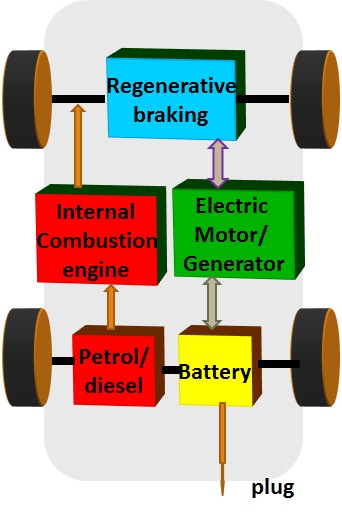
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle like a hybrid electric vehicle has two complimentary drive systems-an electric motor and an ICE to drive the wheels. However, they differ from HEV by having larger battery and allowing the batteries to be charged by plugging in to the grid. This enables to run as BEV when battery power is available or as HEV when battery is low. Thus, in PHEV, the dependence on fossil fuel is greatly reduced. As the battery size is larger than the HEV, the cost of PHEV is more than the HEV.
Some of the PHEV vehicles in market are Audi A3 E-Tron, BMW 330e , Fiat 500e, Ford C-Max Energi, Ford Fusion Energi , Hyundai Sonata , Kia Optima, Toyota Prius prime, Volvo XC90 TB.
References
[1] Global Energy & CO2 Status Report 2019 – Analysis – IEA.
3 thoughts on “Types of Electric Vehicle”