Today everyone is talking about Electric Vehicles (EV) will be our future. For sure, within few years, we will own an Electric Vehicle or we may become an entrepreneur in EV business. So let us understand the basics of Electric Vehicles and the main components of EV before adopting to EV environment.
What do you mean by an Electric Vehicle?
An Electric Vehicle (EV) is a vehicle that uses the electrical energy stored in batteries to supply the electric motors used for propulsion.
Due to the dependence on battery for energy supply, EVs are limited to short range. To increase the range of the vehicle, Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) is included in some EVs.
A Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) is a vehicle that has both ICE and electrical motor for propulsion. Gasoline (petrol) is used for IC engine and batteries for driving the electric motor.
To read more about different types of Electric vehicle
What are the characteristics of EV?
- Electric propulsion system
- Energy storage system
- Zero emission
An Electric Propulsion system provides the necessary power to the wheels. A pure electric vehicle uses electric motor for propulsion while a hybrid electric vehicle uses both electric motor and IC engine for propulsion.
The energy storage system includes a battery. A pure electric vehicle uses the battery power for supplying the motor and during braking battery absorbs the regenerated power. A hybrid electric vehicle uses fossil fuel for IC engine and battery for running the electric motor.
A pure electric vehicle does not produce any emission while a hybrid electric vehicle emits due to the combustion in IC engine.
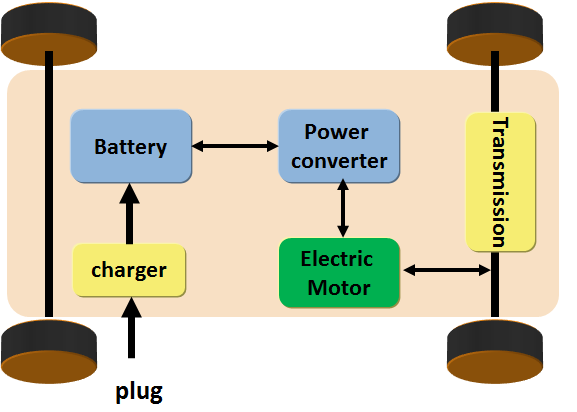
Main components of EV
EVs have fewer moving parts compared to that of an Internal Combustion Engine vehicle. EV have only 20 moving parts while 2000 plus moving parts are available in ICE.
The main components of Electric Vehicle are
- Battery
- Battery Charger
- Power electronic converter
- Electric motor
- Transmission
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU) 1.Battery– The battery is used for storing the energy that moves the vehicle. The battery can be charged from the electric grid and also during regenerative braking. The higher the kW of the battery, the higher the range of vehicle.
2. Battery Charger– The battery charger is basically a rectifier which converters the grid AC power to DC to charge the battery. It can control the current flowing into the battery by controlling the DC voltage. Bidirectional chargers are used in Vehicle to Grid (V2G) mode during which the battery power is fed back to grid.Electric motor provides the necessary torque to move the vehicle.
3. Electric motors-Electric motors can provide torque even at zero speed. This helps to have a single speed transmission to drive the wheels unlike an ICE vehicle which uses multi-transmission system. Electric motors are 90 % efficient while the gasoline powered engines are only 20 % efficient.
4. Power electronic converter – Converts the Direct Current from the battery into alternating Current required to drive the electric motor.
5. Transmission– Transmission transmits the power from the engine to the wheels along the drive shaft and axle. The differential allows to control the different wheels on the same axle such that left and right traction wheels can spin at different speeds during turning.
6. Electronic Control Unit (ECU) –ECU controls all the electrical systems in an electric vehicle. The electric vehicle has multiple sensors to monitor the battery level, vehicle speed, cabin temperature, etc. The ECU collects all these data to control the operation of the electric vehicle effectively.
What is regenerative braking?
In IC engine vehicle, when brake is applied, the kinetic energy is converted into heat. In electric vehicle, on applying brake, the kinetic energy is converted into electrical energy and stored in battery.
How to charge the batteries in electric vehicle?
The batteries can be charged either from the grid directly or from charging stations depending upon the size of the battery in the vehicle. Depending upon the speed at which vehicle is charged,chargers are classified into three types.
- Slow chargers – Slow AC chargers are used to charge electric 2-wheelers, 3-wheelers and 4-wheeler vehicles.
The slow chargers are rated up to 3kW.
Often used to charge overnight at home or at the workplace.
The charging time is usually 8-10 hours.
2.Fast charging – Fast AC chargers are typically rated at either 7Kw or 22kW.
Can be installed in parking area of apartment, shopping area and malls.
Charging time for a 7 kW charger will be around 4-6 hours, while a 22 kW charger may charge the vehicle in 1-2 hours.
3. Rapid chargers – Rapid DC chargers are typically rated from 43 kW.
This is the fastest method to charge an electric vehicle.
Only EVs with compatibility for rapid charging can be charged.
Can be installed in the highways.
Charging time: 30-60 minutes.
References
3 thoughts on “Basics of Electric Vehicle”