Whenever we hear the word “Electrical Engineering” or Electrical Technology, the first thing come to our mind is electricity. Today, the modern world completely relies on electricity.
In this article we will see about the basics of electricity.
Modern Electron Theory
All matters are composed of minute particles called molecules. Each molecule is made up of atoms. An atom is considered to be the smallest unit of a chemical element.
An atom consists of a central nucleus surrounded by electrons.
- Protons are positively charged particles while the neutrons have no charge.
- But, both have the same mass.
- Electrons are negatively charged particles.
- The mass of electrons is very small when compared to the mass of protons and neutrons.
Under ordinary conditions,
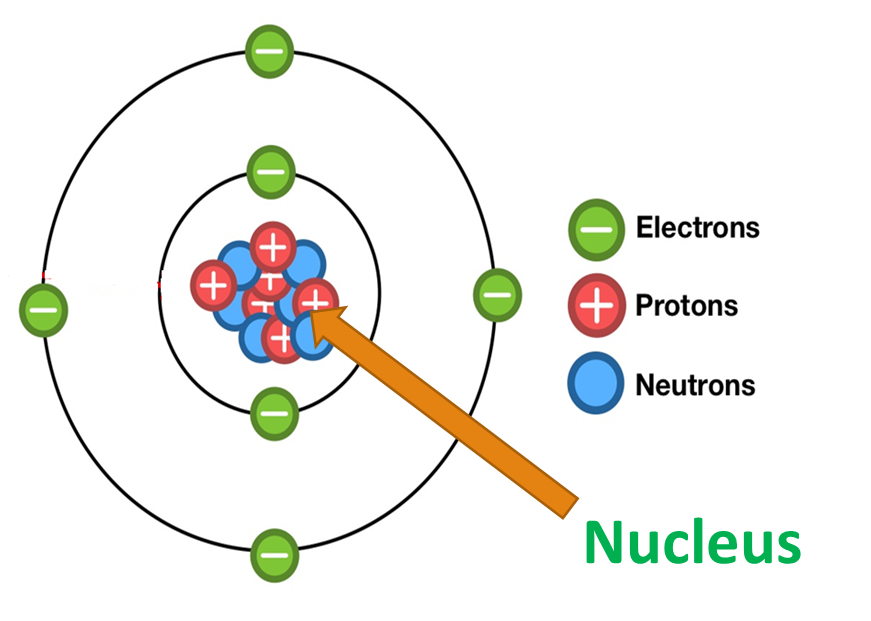
the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons.
Therefore, in normal condition, an atom is said to be neutral ( no charge).
How to attain positive or negative charge?
In a neutral body, number of protons is equal to number of electrons.
If we remove some of the electrons from the neutral body by any process, the resultant body is said to possess a positive charge.
In other words, a body which has deficit of electrons is said to have positive charge.
If we supply some electrons to the neutral body by any process, the resultant body is said to possess a negative charge.
In other words, a body which has excess of electrons is said to have negative charge.
How to measure charge?
The charge on an electron is so small. Instead of measuring the charge of a single electron, the charge on 6.28 x 1018 electrons is measured as 1 coulumb.
1 coulomb = Charge on 6.28 x 1018 electrons.
The symbol for the charge is Q or q.
Electric current
To explain the flow of electric current in a circuit, let us consider a copper strip. A copper strip has a large number of free electrons moving in random direction. At any section of the strip, the net number of electrons crossing the section is zero. Hence, there is no flow of electric current.
When a voltage is applied across the strip, then the free electrons which are negatively charged will start moving towards the positive terminal of the cell. This directed flow of electrons is called electric current.
The actual direction of current, is from the negative terminal to the positive terminal of the cell through the part of the external circuit. However, the conventional current direction is assumed to be from positive terminal to negative terminal.
Electric current- The directed flow of free electrons (or charge)
Closed path is required for current to flow
Unit of current- Ampere
I =Q/t
Where I- current -Ampere
Q- Charge-Coulumb
t-time-sec
Electric voltage or potential
A voltage can exist between a pair of electrical terminals whether a current is flowing or not.For example a battery can show a voltage of 12 V when it is connected to a circuit or not.
A body is said to have an electric potential of 1 volt if 1 joule of work is done in moving 1 coulomb of charge from one point to another.
Voltage – work required to move charge through the element.
Voltage exists under open circuit conditions
SI unit of voltage is Volt
V =W/Q
Where
V- Voltage -Volt
W- Work done- Joules
Q- Charge-Coulumb
If you like the content, do subscribe and like the channel. Please send your feedback to improve the content and suggest a topic for next article.
