In this article we will see about the passive component resistance and the factors affecting the resistance. The effect of temperature on resistance is also highlighted.
What do you mean by resistance?
Resistance is the opposition offered by a substance to the flow of electric current. Higher the resistance lower the current flow in the circuit.
The unit of resistance is ohm.
Ohm is named after the scientist George Simon Ohm who found ohm’s law.
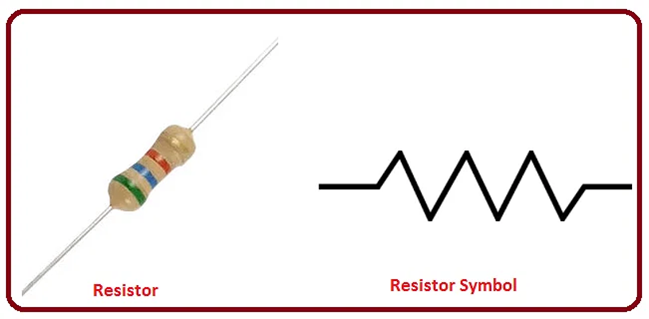
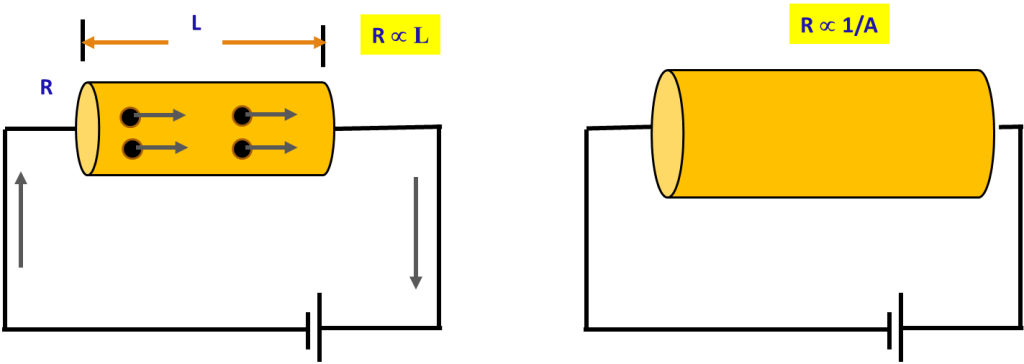
Factors affecting the resistance
R = ρL/A
Where R – ohms (Ω)
ρ –Specific resistance or Resistivity (Ω –m )
L-length of the conductor (m)
A –Area of the conductor (m2)
Conductance
Conductance is the reciprocal of resistance.
G=1/R
G=σ A/L
σ-conductivity ( Siemen/m or mho/m)
Effect of temperature on resistance
The resistance of a material changes with the change in temperature
1.Positive temperature coefficient of resistance
Resistance of the material increases with increase in temperature
Eg. Copper, Aluminium
2. Negative temperature coefficient of resistance
Resistance of the material decreases with increase in temperature
Eg. Insulators, Glass, Mica, Rubber

Temperature co-efficient of resistance
Temperature co-efficient of resistance of a conductor is the increase in resistance per ohm original resistance per °C rise in temperature.
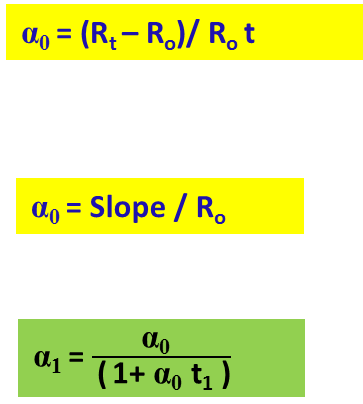
if the content is useful, like the content.Send me your suggestions for improving the content.
- Basic electrical engineering
- choppers
- DC DC converter
- Electric car
- Electric vehicle
- Indian Transport System
- Inverter
- Power Electronics
- Power electronics lecture notes